In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the digital realm has become an integral part of our daily lives. With the convenience and connectivity that technology brings, it also introduces new challenges and risks. The face of cyber threats is constantly shifting, presenting a dynamic and complex environment that demands our attention and vigilance. In this blog, we will explore the changing landscape of cyber threats and discuss what you need to know to stay ahead of the curve.
The Evolution of Cyber Threats
1. Sophistication on the Rise
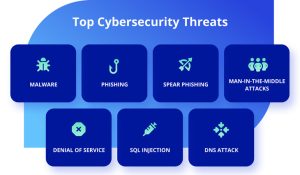
Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, employing advanced tactics and techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. Gone are the days of simple phishing emails; today’s threats involve complex malware, social engineering, and even artificial intelligence to target individuals and organizations.
2. Ransomware Reigns Supreme
Ransomware attacks have seen a significant surge, with cybercriminals targeting businesses, healthcare institutions, and even critical infrastructure. These attacks encrypt valuable data and demand a ransom for its release, causing significant financial and operational damage.
3. Cloud and IoT Vulnerabilities
As organizations migrate to the cloud and embrace the Internet of Things (IoT), new attack surfaces emerge. Securing cloud environments and IoT devices is crucial, as cybercriminals exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and compromise sensitive information.
The Current Cyber Threat Landscape
1. Nation-State Cyber Warfare
The line between cybercrime and cyber warfare continues to blur, with nation-states engaging in cyber-espionage, cyber-attacks, and disinformation campaigns. Understanding geopolitical tensions and the potential for state-sponsored attacks is vital for comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
2. Insider Threats
Insider threats, whether intentional or accidental, pose a significant risk. Employees with access to sensitive information can become unintentional conduits for cyberattacks. Organizations need to implement robust security protocols and continuous monitoring to detect and mitigate insider threats.
3. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The interconnected nature of modern businesses extends vulnerabilities beyond their immediate networks. Cybercriminals exploit weaknesses in supply chains, targeting third-party vendors to gain access to larger networks. Strengthening supply chain cybersecurity is paramount to mitigating these risks.
What You Need to Do
1. Prioritize Cybersecurity Awareness
Education is the first line of defense. Employees and individuals should be well-informed about the latest cyber threats, phishing tactics, and best practices for online security. Regular training sessions can empower individuals to recognize and report potential threats.
2. Implement Robust Security Measures
Organizations must invest in advanced cybersecurity tools and technologies. This includes firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols. Regularly updating and patching systems is essential to address newly discovered vulnerabilities.
3. Foster a Culture of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not just an IT concern; it’s a collective responsibility. Organizations should foster a culture of cybersecurity, encouraging employees to report suspicious activities and promoting a proactive approach to risk mitigation.
4. Collaborate and Share Threat Intelligence
In the face of evolving cyber threats, collaboration is key. Sharing threat intelligence within industries and across sectors helps create a collective defense mechanism. Collaboration enables the swift identification and response to emerging threats.
Emerging Technologies and Future Threats
As we look ahead, emerging technologies bring both promise and peril to the cybersecurity landscape. Artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and 5G networks offer unprecedented opportunities, but they also introduce new vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity professionals must stay abreast of these developments to anticipate and counteract potential threats.
1. AI-Powered Attacks
The same technology that powers cybersecurity defenses is now being harnessed by cybercriminals. AI-driven attacks can automate tasks, adapt to changing circumstances, and evade traditional security measures. Defenders must embrace AI in their strategies to stay ahead of these adaptive threats.
2. Quantum Computing Risks
While quantum computing promises breakthroughs in solving complex problems, it also poses a threat to current encryption methods. Quantum computers could potentially decrypt sensitive information, prompting the need for quantum-resistant encryption protocols to ensure data security in the post-quantum era.
3. 5G and IoT Security Challenges
The rollout of 5G networks accelerates connectivity but brings new security challenges, especially with the proliferation of IoT devices. The massive increase in connected devices amplifies the attack surface, requiring robust security measures to prevent exploitation and unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity Regulations and Compliance
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are recognizing the urgency of addressing cyber threats. As a result, cybersecurity regulations are evolving to enforce stricter standards and compliance requirements. Organizations must stay informed about these regulations to avoid legal consequences and reputational damage.
1. Compliance as a Competitive Advantage
Compliance with cybersecurity regulations is no longer just a legal necessity—it’s a competitive advantage. Businesses that prioritize and demonstrate compliance build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO standards are becoming benchmarks for cybersecurity excellence.
2. Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Regulations often emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring and rapid incident response. Organizations need to invest in monitoring tools, incident response plans, and regular drills to ensure a swift and effective response to cyber incidents.
The Human Element in Cybersecurity
While technological advancements play a crucial role in cybersecurity, the human element remains a pivotal factor. Social engineering tactics, manipulation, and user errors continue to be exploited by cybercriminals. Training and awareness programs must address this human factor to create a more resilient cybersecurity posture.
1. Behavioral Analysis and User Training
Implementing behavioral analysis tools can help identify unusual user activity, potentially signaling a security incident. User training programs should focus not only on recognizing phishing attempts but also on promoting responsible online behavior to reduce the risk of unintentional security breaches.
2. Building a Cyber-Aware Workforce
Organizations should prioritize building a cyber-aware workforce by instilling a sense of responsibility for cybersecurity across all levels. Employees should understand the consequences of their actions on the organization’s overall security posture, fostering a collective commitment to cybersecurity.
In conclusion, the shifting face of cyber threats demands a holistic and adaptive approach. Embracing emerging technologies, staying compliant with evolving regulations, and addressing the human element are integral components of a robust cybersecurity strategy. As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, continuous learning, collaboration, and a proactive mindset will be essential to staying ahead of the ever-changing threat landscape.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Collaboration and Innovation
Looking forward, the battle against cyber threats requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, and individuals alike. Collaboration is paramount in sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and developing innovative solutions.
1. Public-Private Partnerships
Governments and private enterprises must join forces to create a united front against cyber threats. Public-private partnerships enable the sharing of critical information and resources, fostering a collaborative environment to strengthen overall cybersecurity defenses. Initiatives such as information-sharing platforms can enhance collective resilience.
2. Cybersecurity Innovation
In the race between defenders and cyber adversaries, continuous innovation is essential. Investing in research and development for new cybersecurity technologies and strategies is crucial to stay ahead of emerging threats. Start-ups, academia, and established cybersecurity firms play a pivotal role in driving innovation that can reshape the future of cybersecurity.
Personal Cyber Hygiene
Individuals, being the end-users of technology, play a crucial role in cybersecurity. Practicing good cyber hygiene is akin to locking the doors and windows of our digital lives, preventing easy entry for cybercriminals.
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification to access their accounts. This simple step can significantly enhance personal and organizational security, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Regular Software Updates
Keeping software, operating systems, and applications up-to-date is a fundamental yet often overlooked aspect of cybersecurity. Regular updates patch vulnerabilities, closing potential entry points for cyber threats. Automated updates or reminders can streamline this process for users.
Ethical Considerations in Cybersecurity
As technology becomes more deeply ingrained in our lives, ethical considerations in cybersecurity become increasingly crucial. Balancing security needs with individual privacy rights is a delicate challenge that requires thoughtful and responsible decision-making.
1. Privacy by Design
Integrating privacy considerations into the design and development of technologies is an ethical imperative. Implementing a “privacy by design” approach ensures that security measures respect user privacy from the outset, promoting trust and transparency.
2. Responsible Data Handling
Organizations must adopt ethical data handling practices, respecting user consent and safeguarding personal information. Striking a balance between data-driven insights and user privacy is essential for maintaining ethical standards in the cybersecurity landscape.
Conclusion: A Unified Front Against Cyber Threats
The shifting face of cyber threats underscores the need for a unified and adaptive approach. By embracing collaboration, fostering innovation, practicing good cyber hygiene, and prioritizing ethical considerations, we can collectively fortify our defenses against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
In this era of rapid technological advancement, staying ahead of cyber adversaries requires a commitment to continuous learning and improvement. The future of cybersecurity hinges on our ability to adapt, collaborate, and innovate in the face of an ever-changing digital landscape. Together, we can build a more secure and resilient digital future
