Footprinting and Reconnaissance: The First Steps of Ethical Hacking

Welcome to the exciting world of ethical hacking! In this article, we will delve into the crucial initial stages of ethical hacking known as “Footprinting” and “Reconnaissance.” These fundamental steps are essential for any ethical hacker to gain valuable insights and understand their target before initiating further actions. So, let’s explore how these preliminary phases play a vital role in ensuring the success of ethical hacking endeavors.
1.Understanding Footprinting and Reconnaissance
Footprinting and reconnaissance involve the systematic gathering of information about a target system or network. These initial steps are non-intrusive, meaning they do not involve actively exploiting vulnerabilities or attempting unauthorized access. Instead, they focus on using publicly available information to understand the target better.
2.Importance of Footprinting
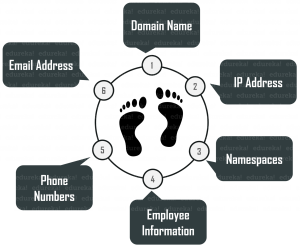
Footprinting is akin to laying the foundation for an ethical hacking operation. It helps hackers identify potential vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and entry points into a target system. By gathering information about the target’s IP addresses, domain names, network infrastructure, and public-facing services, ethical hackers can create a comprehensive picture of the organization’s online presence.
3.Passive Footprinting
Passive footprinting involves using publicly available resources like search engines, social media, and websites to gather information. This method does not interact with the target directly, making it less likely to raise any alarms.
4.Active Footprinting
Active footprinting, on the other hand, involves engaging with the target directly, such as using tools to scan the target’s network for open ports or probing for information. While more intrusive, it provides deeper insights into potential vulnerabilities.
5.Reconnaissance Techniques
Reconnaissance is about actively exploring the target once the initial footprint has been established. Various techniques are employed during this phase, including:
-
Network Scanning
Network scanning involves probing the target’s network to identify live hosts, open ports, and services running on those ports. This information is invaluable for ethical hackers to pinpoint potential entry points.
-
Banner Grabbing
Banner grabbing involves capturing information from network banners or service identification messages. This data often reveals crucial details about the target’s operating systems and software versions, which can be exploited in later stages.
-
Whois Lookup
A Whois lookup provides details about the ownership and registration of domain names, IP addresses, and other related information. Ethical hackers use this data to understand the target’s infrastructure and its relationship with other entities.
-
Social Engineering
Social engineering is the art of manipulating individuals to divulge sensitive information. Ethical hackers may use this technique to gather information that could aid in the hacking process.
6.The Role of OSINT
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) is a significant component of both footprinting and reconnaissance. OSINT involves gathering information from publicly available sources, such as websites, forums, and social media. This data can be analyzed to uncover potential security weaknesses.
7.Ensuring Ethical Practices
While the goal of ethical hacking is to identify vulnerabilities, it is essential to conduct these activities responsibly and within the boundaries of the law. Ethical hackers must seek proper authorization from the target organization and follow strict ethical guidelines to protect the integrity and privacy of the information they access.
8. Ethical Hacking in Today’s Cyber Landscape
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber landscape, ethical hacking plays a critical role in safeguarding digital assets and preserving privacy. With the increasing complexity of technology and the internet, organizations face an ever-growing risk of cyberattacks. Ethical hackers serve as the frontline defense, proactively identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses before malicious hackers can exploit them.
9. Understanding the Ethical Hacker’s Mindset
Ethical hackers possess a unique mindset that combines curiosity, problem-solving skills, and a strong sense of responsibility. They view systems and networks from an attacker’s perspective, seeking to anticipate potential attack vectors. By adopting this mindset, ethical hackers can better understand the adversary’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and devise effective countermeasures.

10. The Legal and Ethical Aspects of Ethical Hacking
Engaging in ethical hacking comes with significant legal and ethical responsibilities. It is essential to act within the boundaries of the law and obtain explicit permission from the target organization before commencing any testing or assessments. Moreover, ethical hackers must handle the information they gather with utmost care, ensuring confidentiality and preventing any unauthorized disclosure.
11. The Benefits of Ethical Hacking for Organizations
Ethical hacking offers numerous benefits to organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can prevent potential breaches, data theft, and costly downtime. Ethical hacking also helps in meeting compliance requirements and building trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
12. Continuous Learning in Ethical Hacking
The world of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. Ethical hackers must dedicate themselves to continuous learning and staying up-to-date with the latest tools, techniques, and best practices. This commitment to knowledge empowers ethical hackers to remain effective and adaptive in their endeavors.
13. Collaboration and Information Sharing
Ethical hacking thrives on collaboration and information sharing within the cybersecurity community. By pooling knowledge and experiences, ethical hackers can collectively strengthen their skills and understanding of emerging threats. Events like hacking conferences, workshops, and online forums provide valuable platforms for such collaboration.
14. The Future of Ethical Hacking
As technology advances, the scope and complexity of cyber threats will undoubtedly grow. The future of ethical hacking will require even more sophisticated techniques and tools to combat these evolving challenges. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation are likely to play crucial roles in assisting ethical hackers in their tasks.
15. Becoming an Ethical Hacker
For individuals intrigued by the world of ethical hacking, the journey begins with a strong foundation in computer science, networking, and cybersecurity concepts. Certifications such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) and Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) can provide formal recognition of expertise in ethical hacking.
Ethical hacking stands as an essential practice in fortifying digital defenses and preserving the integrity of online systems. Footprinting and reconnaissance serve as the initial steps in this captivating journey, empowering ethical hackers to gain valuable
16. The Ethical Hacker’s Impact on Cybersecurity
The impact of ethical hacking on cybersecurity cannot be overstated. By identifying and rectifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them, ethical hackers act as a proactive line of defense. They help organizations prevent potential data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage, thereby saving businesses and individuals from significant harm.
17. Ethical Hacking vs. Malicious Hacking
It is essential to distinguish between ethical hacking and malicious hacking. Ethical hackers work with the consent of the target organization and adhere to strict guidelines, ensuring that their actions are solely aimed at improving security. Malicious hackers, on the other hand, act without permission and with harmful intent, seeking personal gain or causing harm to others.
18. The Legal Protection of Ethical Hackers
To facilitate ethical hacking practices, many countries have implemented laws that protect hackers when they are operating within the bounds of ethical guidelines and with explicit authorization. These legal protections offer reassurance to ethical hackers and encourage responsible vulnerability disclosure.
19. The Role of Organizations in Embracing Ethical Hacking
For organizations, embracing ethical hacking is a proactive step towards safeguarding their digital assets. By engaging ethical hackers for regular security assessments, organizations can continuously improve their cybersecurity defenses and demonstrate a commitment to protecting customer data.
20. Ethical Hacking and Data Privacy
Data privacy is a paramount concern in today’s digital world. Ethical hackers, while performing their assessments, must prioritize data privacy and ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and secure. Compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is crucial in this regard.
21. Ethical Hacking for Small Businesses
Ethical hacking is not limited to large corporations; it is equally important for small businesses. In fact, smaller entities may be more vulnerable to cyber threats due to limited resources and less robust security measures. Engaging ethical hackers can help small businesses fortify their defenses without breaking the bank.
22. The Human Element in Ethical Hacking
While technology plays a significant role in ethical hacking, the human element is equally crucial. The ability of ethical hackers to think creatively, anticipate attacker behavior, and leverage social engineering techniques underscores the value of human intelligence in cybersecurity.
23. The Global Impact of Ethical Hacking
In today’s interconnected world, the impact of ethical hacking extends beyond individual organizations. By improving cybersecurity practices worldwide, ethical hackers contribute to a safer digital environment for everyone. Their efforts help protect critical infrastructure, government systems, and personal data on a global scale.
24. Challenges Faced by Ethical Hackers
Ethical hacking is not without its challenges. Ethical hackers must navigate complex legal and ethical considerations, and they may encounter resistance from some organizations hesitant to engage in vulnerability assessments. However, perseverance and commitment to the greater cause enable ethical hackers to overcome these obstacles.
25. The Ethical Hacker Community
The ethical hacker community is a vibrant and diverse group of professionals united by their passion for cybersecurity and ethical conduct. They actively share knowledge, exchange experiences, and collaborate to advance the field of ethical hacking collectively.
26. A Never-Ending Journey
In conclusion, ethical hacking represents a never-ending journey in the quest for a more secure digital world. As technology evolves, so will the challenges and threats faced by organizations and individuals. Ethical hackers, armed with their expertise, dedication, and ethical principles, will continue to stand as a bulwark against cyber threats, ensuring that we stay one step ahead of the adversaries. Embracing ethical hacking as a fundamental practice is not only prudent but essential in our interconnected and technology-driven society. Let us all play our part in creating a safer cyber landscape for generations to come.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Always seek the guidance of certified professionals for specific cybersecurity needs and concerns.
